Flying into the Future: How Meteodrones Are Transforming Weather Prediction
Image: Fotokostic/Shutterstock.com
In the ever-evolving field of meteorology, the quest for more accurate and timely weather predictions has led to significant technological advancements. Among these, the development of Meteodrones stands out as a transformative innovation, enhancing our ability to monitor and understand atmospheric conditions. These sophisticated weather drones are redefining data collection methodologies, offering unprecedented insights into the Earth’s lower and middle atmosphere.
Traditional weather forecasting has long relied on ground-based stations and weather balloons to gather atmospheric data. While effective to a degree, these methods present limitations in spatial coverage and frequency, particularly in capturing the dynamic processes of the planetary boundary layer—the lowest part of the atmosphere where most weather events occur. Recognizing these gaps, Meteomatics, a Swiss weather technology company founded in 2012, pioneered the development of Meteodrones. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are designed to collect high-resolution, real-time atmospheric data, thereby enhancing the accuracy of weather models and forecasts.
Meteodrones are engineered to ascend up to 6 kilometers, systematically measuring critical meteorological parameters such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind speed, and wind direction. This capability addresses the observational void in the lower atmosphere, providing data that is often unattainable through conventional means. Equipped with heated rotor systems to prevent icing, Meteodrones can operate in adverse weather conditions, including fog and clouds, ensuring consistent data collection regardless of environmental challenges.
Integration into Weather Prediction Models
The integration of Meteodrone data into numerical weather prediction (NWP) models has demonstrated a marked improvement in forecasting accuracy. By providing high-resolution vertical profiles of the atmosphere, Meteodrones supply essential data that enhances the initialization of NWP models, leading to more precise predictions of weather phenomena such as thunderstorms and fog. This advancement is particularly beneficial for anticipating high-impact weather events, thereby bolstering preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Global Deployments and Collaborations
The versatility and efficacy of Meteodrones have led to their adoption in various international projects aimed at improving weather forecasting and climate resilience.
Norway’s Nationwide Weather Network
In Norway, a network of 30 Meteodrones and Meteobases is being established to enhance the country’s weather prediction capabilities. This initiative, part of a national strategy, underscores the commitment to leveraging advanced technology for better weather forecasting, which is crucial for sectors such as agriculture, aviation, and emergency services.
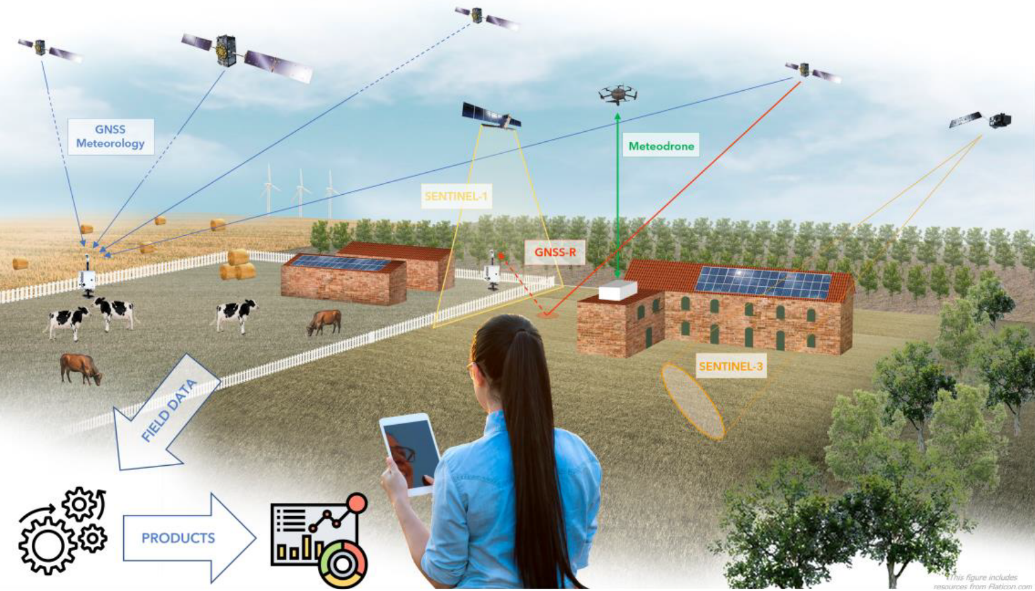
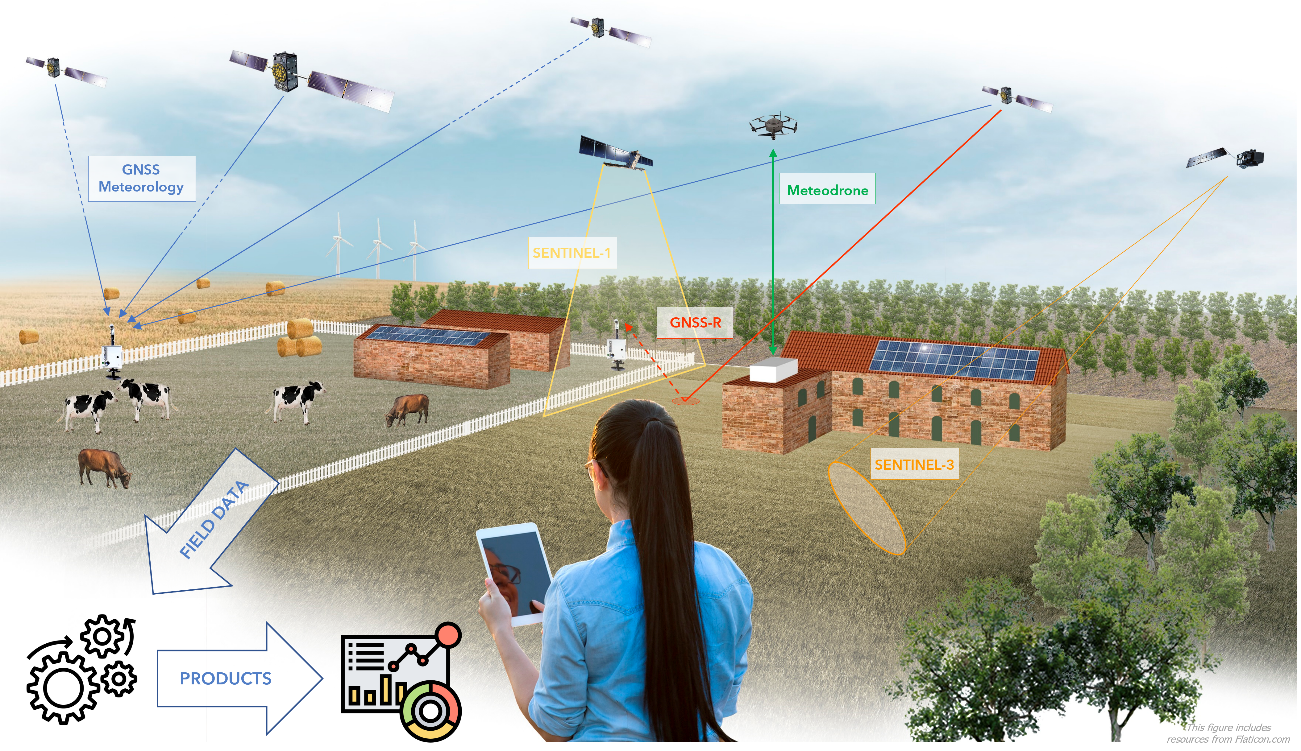
Agricultural Applications in France, Italy and Romania
In France, Italy and Romania, as part of the MAGDA project, Meteodrones are being deployed to assist farmers in mitigating weather-related risks exacerbated by climate change. By collecting localized weather data, these drones contribute to more accurate forecasts, enabling farmers to protect their crops from adverse conditions like frost, hail, and heatwaves, thereby ensuring better harvests and sustained agricultural production.
U.S. Weather Monitoring Initiatives
In the United States, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is evaluating the use of Meteodrones for atmospheric data collection. These drones gather critical information on temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind conditions, offering a promising alternative to traditional methods like weather balloons. The goal is to enhance the accuracy of weather forecasts and warnings, particularly for severe weather events.
The trajectory of Meteodrones points toward a future where high-resolution, real-time atmospheric data becomes integral to various sectors. As technology advances and regulatory frameworks evolve, the deployment of Meteodrones is expected to expand, further enhancing our ability to predict and respond to weather events. Their role in projects like MAGDA, which aims to improve site-specific weather forecasts and irrigation advisories to protect crops from severe weather impacts, exemplifies the broader applications of Meteodrones in addressing climate-related challenges.
Meteodrones represent a significant leap forward in meteorological data collection, offering solutions to longstanding challenges in weather forecasting. By providing high-resolution, real-time data from the lower atmosphere, they enhance the accuracy of weather models, contribute to better preparedness for severe weather events, and support various sectors, from agriculture to aviation. As their deployment becomes more widespread, Meteodrones are poised to play a pivotal role in our ongoing efforts to understand and adapt to the complexities of the Earth’s atmosphere.
Author: Akemi Narindal-Aoki, PhD